Monday 14 May 2018
Wednesday 9 May 2018
Monday 7 May 2018
Neonatal Reflexes
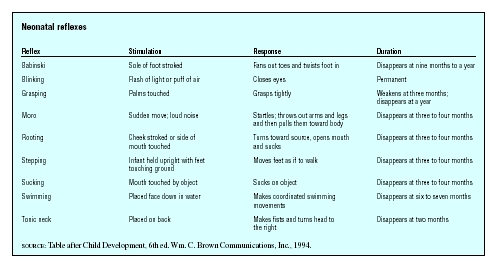
- Neonatal reflexes
(Table by GGS Information Services.)Reflex Stimulation Response Duration SOURCE : Table after Child Development, 6th ed. Wm. C. Brown Communications, Inc., 1994. Babinski Sole of foot stroked Fans out toes and twists foot in Disappears at nine months to a year Blinking Flash of light or puff of air Closes eyes Permanent Grasping Palms touched Grasps tightly Weakens at three months; disappears at a year Moro Sudden move; loud noise Startles; throws out arms and legs and then pulls them toward body Disappears at three to four months Rooting Cheek stroked or side of mouth touched Turns toward source, opens mouth and sucks Disappears at three to four months Stepping Infant held upright with feet touching ground Moves feet as if to walk Disappears at three to four months Sucking Mouth touched by object Sucks on object Disappears at three to four months Swimming Placed face down in water Makes coordinated swimming movements Disappears at six to seven months Tonic neck Placed on back Makes fists and turns head to the right Disappears at two months
Thursday 3 May 2018
Commonest malignancies
Commonest malignancies (Worldwide) –
- In children – leukemia
- In females – breast cancer
- In males – prostate cancer
- Overall – breast cancer
- Children - leukemia
- Male - oral
- Female – CA cervix
- Commonest variety of breast cancer – invasive ductal
- Commonest origin of Oral cavity, tongue, skin, cervix malignancies – squamous cell CA
- Commonest origin of Breast, pancreas, gall bladder, endometrium malignancies –scirrhous adeno CA
- Breast CA – More in left
More in upper outer quadrant
Origin – ductal epithelium commonly
- TNM classification Adenocarcinoma is of 2 types – lobular and ductal(commonest)
- Leiomyoma – Benign/fibroid tumour of uterine myometrium
- Types -
- Intramural/interstitial – within uterine wall, generally asymptomatic, most common type.
- Subserosal/subperitoneal – under mucosal peritoneal surface, grows on outer wall of the uterus.
- Submucosal – just below the lining of the uterus, under endometrium.
- Pedunculated – sub-serosal with peduncle.
Wednesday 2 May 2018
Tuesday 1 May 2018
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)














